Everything you need to know about scoliosis and treatment options
Scoliosis can impact individuals of all ages, from young children to older adults, and varies widely in severity. While some may only notice minor discomfort, others may experience more pronounced shifts in posture or mobility. Identifying the condition early is essential for management and timely treatment. Visiting a dedicated scoliosis clinic in Queensland will help ensure you receive an individualised care plan based on your unique condition.

What a Scoliosis?

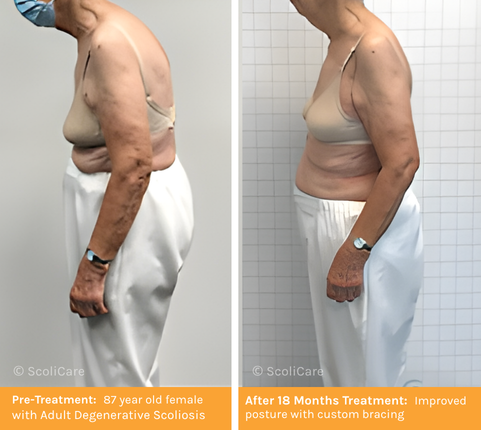
Scoliosis is often thought of as a condition that only affects teenagers. In fact, it can develop at any time. In adults, scoliosis can develop from a previously undiagnosed childhood condition or occur later in life due to degenerative changes in the spine. While some adults experience mild symptoms, others may see the curve worsen over time, potentially affecting mobility and quality of life. Early intervention with custom bracing and scoliosis specific rehabilitation can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
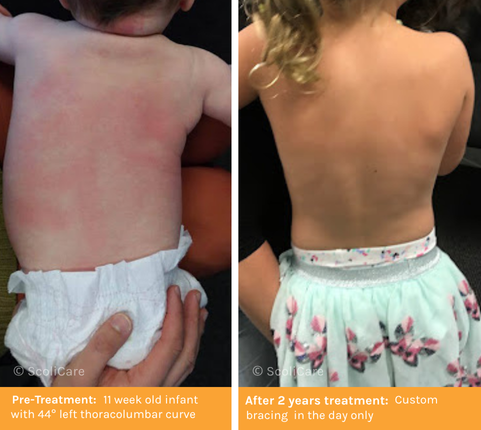
What is Infantile Scoliosis?

Infantile scoliosis occurs in children under the age of 4, usually presenting as a left-sided curve. While many cases may resolve naturally as the child grows, some can worsen over time, potentially leading to more serious problems. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing progression. Treatment options vary based on the severity of the curve and may include monitoring, casting, custom bracing, and in severe cases, surgery.
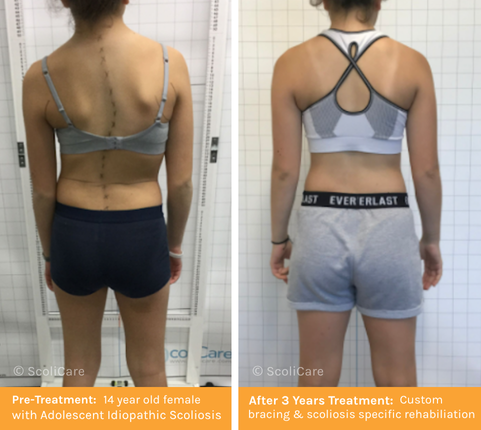
What is Adolescent Scoliosis?

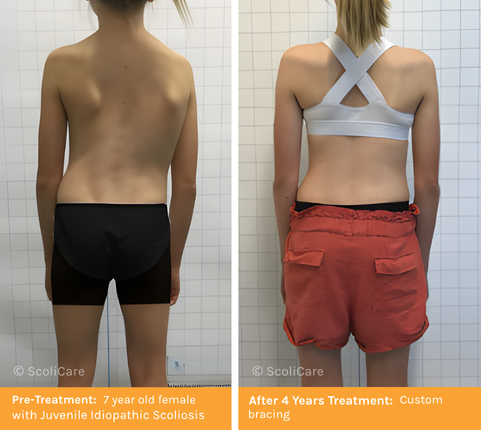
What is Juvenile Scoliosis?

Juvenile scoliosis is a type of idiopathic scoliosis that affects children between the ages of 4 and 10 years of age. It is more common in girls, particularly between ages 6 and 10. The condition often worsens over time, with a higher risk of progression if not detected and treated early. In many cases, treatments such as custom bracing and scoliosis specific exercise rehabilitation are available as evidence-based treatment options for patients with Juvenile Scoliosis.
What is Infantile Scoliosis?

Infantile scoliosis occurs in children under the age of 4, usually presenting as a left-sided curve. While many cases may resolve naturally as the child grows, some can worsen over time, potentially leading to more serious problems. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing progression. Treatment options vary based on the severity of the curve and may include monitoring, casting, custom bracing, and in severe cases, surgery.
What is Scoliosis?

Scoliosis is a progressive spinal condition where the spine curves, forming a “C” or “S” shape. While the spine naturally curves when viewed from the side, it should appear straight from behind. Common signs include uneven hips or shoulders, a visible curve in the spine, a forward lean, or persistent back pain.
This condition can develop at any age, from infancy to adulthood, and the effects depend on how early it appears and how severe it becomes. Detecting scoliosis early is key for getting the best possible treatment outcomes. Routine checks are important for all age groups to ensure timely diagnosis and intervention where needed.
What is Scoliosis?

Scoliosis is a progressive spinal condition where the spine curves, forming a “C” or “S” shape. While the spine naturally curves when viewed from the side, it should appear straight from behind. Common signs include uneven hips or shoulders, a visible curve in the spine, a forward lean, or persistent back pain.
This condition can develop at any age, from infancy to adulthood, and the effects depend on how early it appears and how severe it becomes. Detecting scoliosis early is key for getting the best possible treatment outcomes. Routine checks are important for all age groups to ensure timely diagnosis and intervention where needed.
What is Scoliosis?

Scoliosis is a progressive spinal condition where the spine curves, forming a “C” or “S” shape. While the spine naturally curves when viewed from the side, it should appear straight from behind. Common signs include uneven hips or shoulders, a visible curve in the spine, a forward lean, or persistent back pain.
This condition can develop at any age, from infancy to adulthood, and the effects depend on how early it appears and how severe it becomes. Detecting scoliosis early is key for getting the best possible treatment outcomes. Routine checks are important for all age groups to ensure timely diagnosis and intervention where needed.
The benefits of non-surgical treatment
Treating scoliosis begins with a personalised evaluation of the spine, curve severity, and overall health goals. Non-surgical treatments like scoliosis-specific exercises and custom bracing can offer significant benefits, aiming to stabilise the spine, support posture, reduce pain, and prevent further curve progression where possible. When the curve is severe or rapidly progressing, surgery may be the recommended option. The best possible outcomes come from working with a dedicated scoliosis clinician who can guide patients through a customised care plan.

FAQ’s
Here are some commonly asked questions around Scoliosis and available treatments: